|
|
|
You can get e-magazine links on WhatsApp. Click here
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fruit juices - Excellent sources of vitamins, minerals, phytonutrients
|
|
Friday, 06 November, 2020, 14 : 00 PM [IST]
|
|
Dhanavath Srinu
|
1. Introduction
India produces most of the fruits and vegetables and is the second-largest producer in the world after China. The major export destinations for Indian fruits and vegetables are Bangladesh, the UAE, Pakistan, Malaysia, Sri Lanka, the UK, Saudi Arabia, and Nepal.
India's share in the global market for processed fruit and vegetable products ranges from 1-2% only. The prominently processed fruit-based products in India are juice, ready to serve (RTS) beverages, pulp, squash, ketchup, concentrate, canned fruits, jam, jelly, pickles, chutneys, and frozen products. The number of fruit and vegetables processing units in India are 5,293, in which large-scale units are 13% (30 tonne/h) and cottage and small scale industries are 75% (250 tonne/annum).
2. What consumers looking from fruit juices? Fruit juice is defined as the unfermented juice, which is intended for direct consumption obtained by means of mechanical process from sound, ripe fruits. Fruit juices are excellent sources of vitamins, minerals and phytonutrients such as carotenoids, polyphenols and flavonoids. People choose juices for many reasons, including relieving thirst, refreshment, nutritional benefit, health benefit, sports drink, and as an alternative to synthetic drinks.
3. Classification of fruit juices a. Pure fruit juice: It is the natural juice or unfermented juice, pressed out of the fruit and unaltered in composition.
b. Fruit juice beverage: It is a fruit juice that is considerably altered in composition before consumption.
c. Fermented fruit juice: It is a fruit juice that has undergone alcoholic fermentation.
d. Carbonated fruit juice: It is a fruit juice or pulp-based fruit beverage that provides a nutritional element of fruit in addition to the carbonation effect.
e. Squash: It is a drink or juice made from fruit by adding sugar and water. It consists of moderate quantities of fruit pulp.
f. Cordial: It is a sparkling, clear sweetened fruit juice from which all the pulp and other suspended materials have been eliminated.
g. Sherbet or syrup: It is clear sugar syrup that has been artificially flavoured.
h. Fruit juice concentrate: It is a fruit juice that has been concentrated by the removal of water either by heat or by freezing.
i. Fruit juice powder: It is fruit juice which has been converted into a free-flowing, highly hygroscopic powder to which natural fruit flavour in powder form is incorporated to compensate for any loss of flavour.
The FPO specifications and preservation methods of various fruit-based products are given in Table 1:
|
Classification
|
Min.
Juice (%)
|
Min.
TSS (%)
|
Methods
of preservation
|
|
Natural Juice
|
100
|
Natural
|
Canning, Heat, Chemicals
|
|
Sweetened Juice
|
85
|
10
|
Canning, Heat, Chemicals
|
|
RTS beverage
|
10
|
10
|
Heat, Chemicals
|
|
Squash
|
25
|
40
|
Chemicals
|
|
Cordial
|
25
|
30
|
Chemicals
|
|
Crush
|
25
|
55
|
Chemicals
|
|
Syrup
|
25
|
65
|
Chemicals
|
|
Nectar
|
20
|
15
|
Heat
|
|
Fruit juice concentrate
|
100
|
32
|
Chemicals, Aseptic packaging
|
The extraction of juice and pulp from fruits was given in Figure 1.
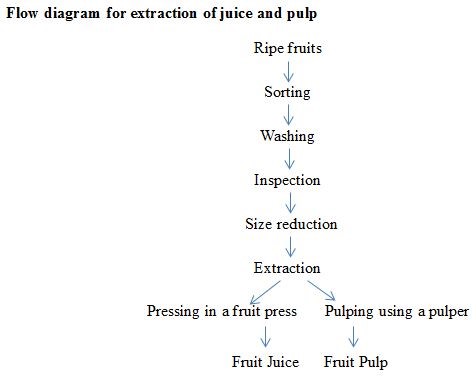
Figure 1. Extraction of juice and pulp
The production of bottled fruit juice was given in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Production of bottled fruit juice
The production of RTS beverage, squash, syrup, and cordial was given in Figure 3.
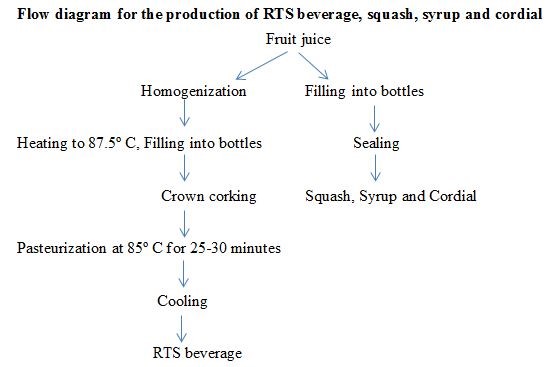 The extraction of juice and pulp from fruits was given in Figure 1.
4. Health benefits of fruit juices
Fruit juices are treasures of micronutrients, antioxidants, and phytochemicals, which have several health benefits such as: Strengthen immune system; Help in detoxification; Cardiovascular benefits; Cancer preventive effect.
5. Conclusion Fruits are rich source of vitamins and minerals. Fruits in the form of various products upon consumption provide a wide range of antioxidants, which boost the health of an individual. Eating a diet high in fruits can reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, inflammation, and diabetes.
(The author is Ph.D. scholar, College of Food and Dairy Technology-TANUVAS, Chennai)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|